文章內容
Principle of Blockchain


❒ BTC ledger
BTC ledger is linked with blocks one by one into a chain, so this technique is called “Blockchain.” As shown in Fig.1, each block is recorded with the payer, the payee, and the transaction amount. Each block may be recorded with a plurality of transactions and blocks will be chained together. For example, Block 3 is chained to Block 2, to Block 1, and finally to Block 0.
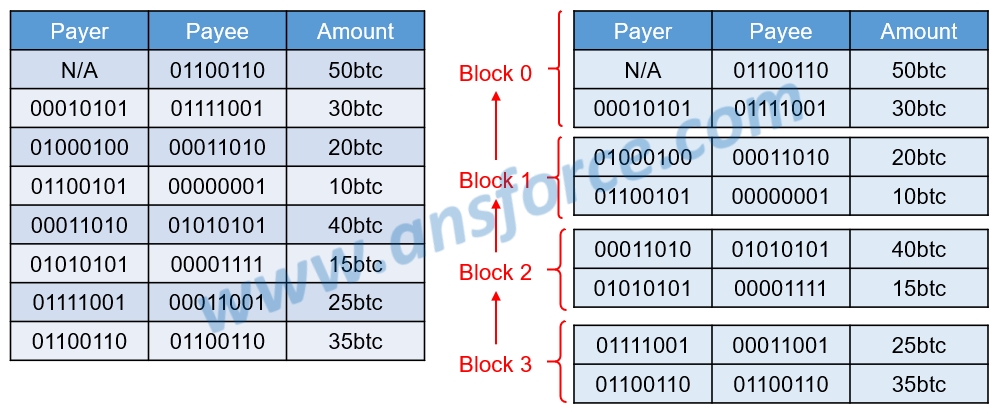 Figure 1: BTC ledger
Figure 1: BTC ledger
Source: Du, H. Y. (2016) : Past, Present and Future of Blockchain, TAIWAN-CA Inc.
Fig.1 is only an illustration. Actually, BTC ledger is not a spreadsheet as Excel. Basically, bitcoin is a virtual electronic currency, so BTC ledger is actually a computer program having many columns, as shown in Fig.2, including:
➤ Hash
“hash”: using Hash algorithm to calculate Hash value
➤ Header
“previousblockhash”: Hash value of previous block
“difficulty”: Hash must be less than the difficulty index
“time”: representing the time when the block was formed and in UNIX format
“nonce”: calculating the parameters to be used by Hash value
“merkleroot”: storing the Summary of Transaction
➤ Transaction
“tx”: the column for storing Transaction, each block may be stored with multiple transactions
➤ Others
“confirmations”: indicating this block has been confirmed by 35,561 nodes!
“height”: indicating this block is the 277,316th block in the sequence of bitcoin blockchain
.jpg) Figure 2: BTC ledger
Figure 2: BTC ledger
Source: Du, H. Y. (2016) : Past, Present and Future of Blockchain, TAIWAN-CA Inc.
❒ Hash algorithm
Hash algorithm is a method to generate “Digital fingerprint” from data, which may convert the original data of any length into a “Hash value” with shorter length and make it difficult to reversely deduce the original data from Hash value, just like encrypting the original data. A certain section of data is corresponded to a certain Hash value and different data has different Hash value, just like different people having different fingerprints, so-called “Digital fingerprint.” There are three common types of Hash algorithms:
➤ Message Digest (MD): MD2, MD3, MD4, MD5, etc.
➤ Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA): SHA-0, SHA-1, SHA-2(SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512), SHA-3, etc.
➤ RIPEMD-160: RACE Integrity Primitives Evaluation Message Digest
For example, Alice paid Bob 10 dollars. This transaction was recorded in electronic document and both of them possessed a copy. Then, Alice tampered the record as “Alice paid Bob 5 dollars.” Although Alice submitted the original electronic document, both parties might stick to his own version and nobody could judge which copy is the correct version. Therefore, how can we prove Alice had tampered the document? As shown in Fig.3, assuming using Hash algorithm, SHA-256, to calculate the Hash value of electronic document “Alice paid Bob 10 dollars” as “01011010,” if the electronic document had been tampered as “Alice paid Bob 5 dollars,” the Hash value would be “01011011.” We only need to compare the Hash values to confirm if the document had been tampered.
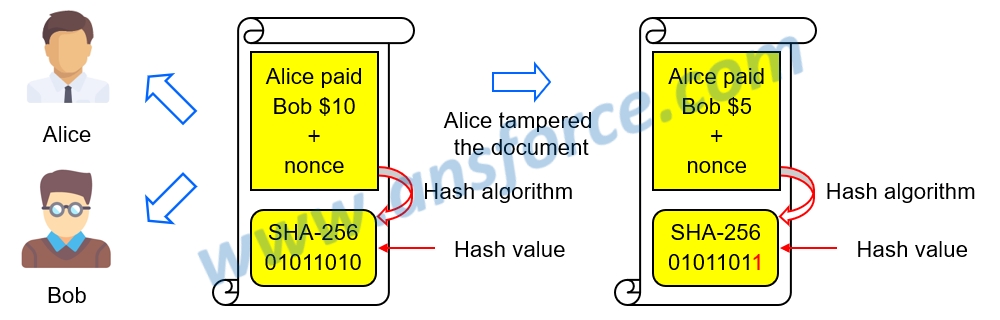
Figure 3: Hash algorithm
Icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com
❒ Meaning of Block
The “Block” refers to a set of data in a computer that is stored in a predetermined column and format. The BTC ledger in Fig.2 may be considered as a block. The goal is to “block” the data in this block to prevent people from tampering. The protection mechanism of BTC ledger is as follows:
1. Store the Summary of Transaction data in the column of “merkleroot”
2. Calculate the Header with Hash algorithm (SHA-256) and store in the column of “hash”
3. If someone wants to edit the transaction (tx), the merkleroot must be re-generated.
4. If someone wants to re-generate the merkleroot, the Hash value must be re-calculated.
5. If the Hash value could not be re-calculated, the transaction (tx) could not be edited.
6. The data in the block can be blocked using the aforementioned mechanism.
However, if the “re-calculating Hash value” could be easily done, the whole protection mechanism would be ineffective. Therefore, scientists invented the “Conditional hash,” which specifies the “Hash” must be less than the “Difficulty” to make the “Hash” very difficult to be re-calculated, so as to protect the content of “Transaction” from tampering.
❒ Bitcoin mining
Speaking of Bitcoin, it would be commonly heard that many people are “mining” on the network. What is exactly bitcoin mining? First, the procedures of bitcoin mining are described as follows:
1. Guess a “nonce” value
2. Use Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) to calculate “Hash”
3. If the calculated “Hash” is less than the “Difficulty,” a block would be successfully created and 50btc would be rewarded.
4. If the calculated “Hash” is larger than the “Difficulty,” repeat the steps above.
The operation of “guessing nonce value” and “calculating Hash” is called “Mining.” The mine to be dug is to calculate one “block” having its “Hash” less than “Difficulty.” The found block may enclose (block) the “Transaction.” The people conducting the mining is called “miner.” Calculating one block may be rewarded 50btc. If the surcharge is charged for other payment transaction, the miner can also get the surcharge. The design for Bitcoin is “mining one block” for about every 10 minutes. The reward will be halved once mining 210k blocks (about four years). Thus, the total number of Bitcoins will not exceed 21 millions (btc). The fixed number of Bitcoins may raise its value.
< Brainstorm >
The bitcoin miner can be rewarded 50btc for calculating one block. One block may be mined for about every 10 minutes. The reward will be halved once mining 210K blocks (about four years). Is there anyone tries to figure out why the total number of Bitcoins will not exceed 21 millions (btc)? (Hint: This is actually an infinite geometric sequence!)
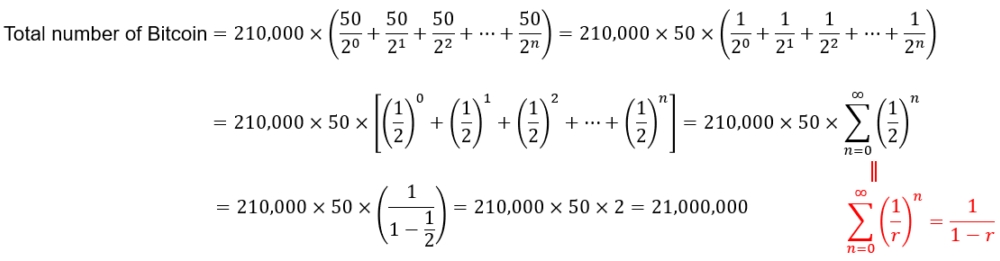
In 2009, Bitcoin rewarded the miner with 50btc. The reward was halved to 25btc at the first time in December, 2012. And, the reward was again halved to 12.5btc at the second time in July, 2016. The decrease of reward caused the surcharge becoming the incentive for mining. In order to maintain “mining” one block for about every 10 minutes, the difficulty of generating new block will be regularly adjusted, that is, for each mining of 2,016 blocks (about two weeks), the mining difficulty will be automatically adjusted for the next 2,016 blocks. Bitcoin miners employed Intel or AMD CPUs (Central Processing Unit) for mining in the early stage. Since 2013, miners started using GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), and even ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit), which resulted in that individual miners could not gain any earings.
❒ Meaning of Chain
The Chain of Blockchain refers to chain different blocks with “hash” and “previousblockhash,” so as to greatly enhance the data security. As shown in Fig. 4, the Header of each block has a column “Previousblockhash.” The Hash of previous block is placed into the Header of the following block. The Header is used to calculate the Hash of this block. Thus, the previous block and the following block are “chained.”
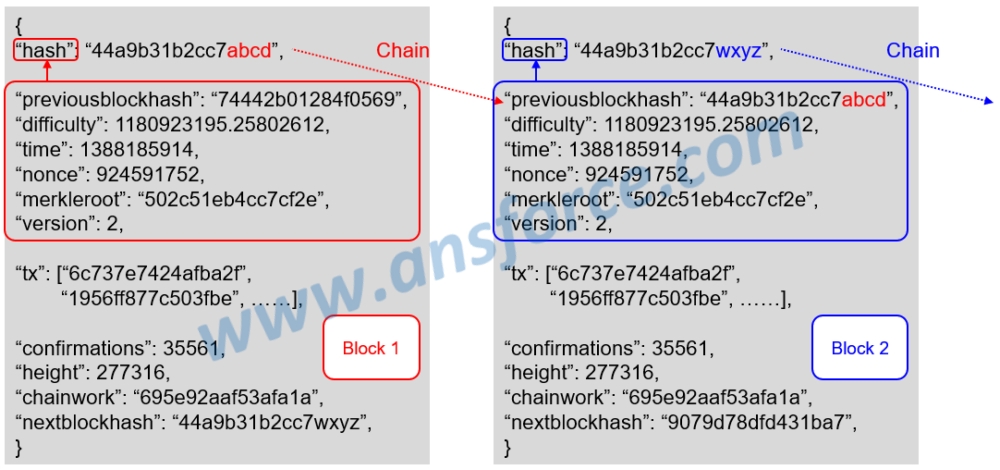
Figure 4: Meaning of Chain.
If someone wants to tamper the “Transaction” in Block 1, he has to re-calculate the Hash of Block 1 because the transaction will affect the “merkleroot” in the Header. The Hash of Block 1 is stored in the “previousblockhash” in the Header of Block 2, so the Hash of Block 2 must be re-calculated, and so on.
If the blockchain has 100 blocks, the Hash would be re-calculated 100 times for tampering the Transaction in one block that would be impossibly done within a reasonable time period. This method enables the whole blockchain being affected by a slight move. Therefore, when the blockchain becomes longer, the previous blocks will be more secured. Besides, each node possess the BTC ledger, so it is no use to tamper only one node.
In a summary, the “Block” refers to a set of data in a computer which is stored in a predetermined column and format. We utilize “Conditional hash”, that is, the calculated Hash must be less than the Difficulty, to block the data in this block. Blocks are chained together with “hash” and “previousblockhash”, so the whole blockchain would be affected by a slight move, and would be impossibly tampered within a reasonable time period. Now, can you really understand the meaning of Blockchain? When you heard someone talking about blockchain, you may ask him what the “Block” is and what the “Chain” means? If he could not answer, you may share this article with him.
【Remark】The aforementioned contents have been appropriately simplified to be suitable for reading by the public, which might be slightly differentiated from the current industry situation. If you are the expert in this field and would like to give your opinions, please contact the writer. If you have any industrial and technical issues, please join the community for further discussion.
