文章內容
Hardware architecture of Processor


❒ What is an architecture?
The term “Architecture” is usually applied in engineering, basically indicating the composition of an object, possibly hardware or software. “Computer organization and architecture” introduces what the components are in the hardware composition of a computer, usually a processor. “Android software architecture” introduces what the programs are in the software composition of Android operating system.
❒ Hardware architecture
Hardware architecture of processor means the internal structure of a processor, which mainly comprises four portions: a control unit (CU), an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), registers and bus as shown in Fig. 1. These four portions are located inside a processor and cannot be seen from outside. They can be only seen by detaching the processor (integrated circuit) and amplifying using an electron microscope.
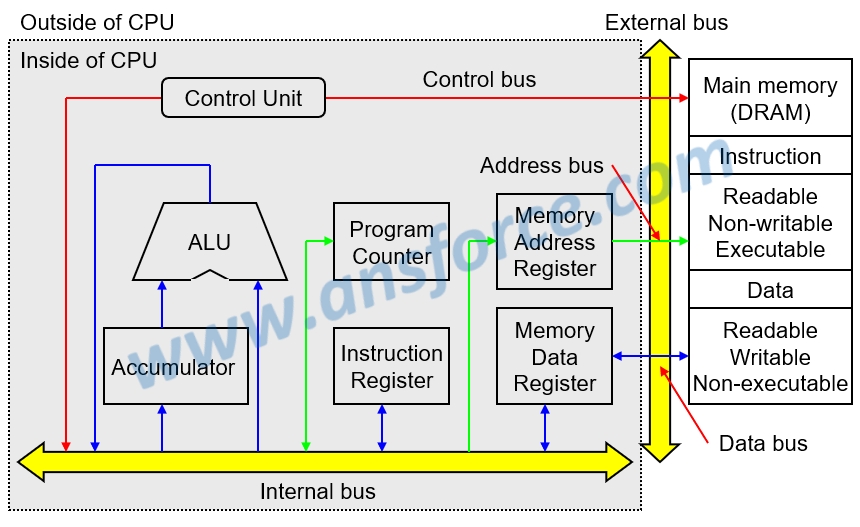
Figure 1: Architecture of a processor.
❒ Control Unit (CU)
Control Unit is inside a processor and sends the control signals in sequence according to the program request, such as Read, Write, for control functions. The Control Unit is the most complicated and difficult part for design.
❒ Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Arithmetic Logic Unit is inside a process providing the calculation functions, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. It should be noted that the title of CPU of a personal computer in the early stage was “Micro processor” meaning its ALU can only execute the addition, and the subtraction can only be executed using addition and complement. Multiplication and division are very difficult processes for a micro processor and must be executed using addition and offset. A computer having such a micro processor was called a micro computer. The ordinary personal computers we use nowadays can only be counted as a “micro” computer. Due to decades of continuous technology progresses, CPU may become so powerful today.
An ordinary ALU can only handle the operation for integer (fixed point number). A Floating Point Unit (FPU) must be added in order to speed up the operation for numbers with decimal points. Furthermore, scientists invented a Digital signal processor (DSP) having an ALU capable of executing multiplication and addition simultaneously to possess more powerful operation capability, which will be introduced later.
❒ Register
The memory having the fastest access speed inside a processor is called Register, which can store data temporarily or used for configuring hardware parameters while an engineer is writing the firmware. The register may be categorized into many different types according to the stored content:
➤ Accumulator (ACC): used for temporarily storing the data after calculation.
➤ Program Counter (PC): used for temporarily storing the address of next instruction or data. www.ansforce.com
➤ Instruction Register (IR): used for temporarily storing the instruction to be executed.
➤ Memory Address Register (MAR): used for temporarily storing memory address.
➤ Memory Data Register (MDR): used for temporarily storing data.
As shown in Fig. 1, during operation, the processor must cooperate with the main memory (DRAM/SDRAM/DDR) and the instructions and data required during operation are all stored in the main memory. The characteristics of instruction and data are as follows:
➤ Instruction: meaning the hardware instructions used during processor operation, such addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. The characteristics of hardware instruction are readable, executable, but non-writable. In other words, the hardware instructions are fixed and cannot be changed (non-writable) after the processor was made.
➤Data: meaning the data used during processor operation. The characteristics of data are readable, writable, but non-executable. In other words, the data can be changed (writable) any time.
Either the instruction or the data stored in the main memory (DRAM/SDRAM/DDR) must have a corresponding address with which CPU may search these instructions and data based on the address. Just like every student in a school must have a student ID, the teacher can easily find the student based on student ID>
❒ Bus
The transmission interface connecting two different electric components for transmitting electric signals is generally called “Interface” or “Bus” that can be divided as External bus and Internal bus:
➤ External bus: The bus may be directly seen by human eyes outside the integrated circuit (IC). As shown in Fig. 1, the external bus is used for connecting CPU with main memory (DRAM). The external bus used by CPU of personal computer has three types: Control bus, Address bus, and Data bus.
➤ Internal bus: The bus cannot be directly seen by human eyes inside the IC (must be seen by detaching IC and amplifying using electron microscope). The internal bus shown in Figs. 1 is used for connecting CU, ALU, and registers.
【Remark】The aforementioned contents have been appropriately simplified to be suitable for reading by the public, which might be slightly differentiated from the current industry situation. If you are the expert in this field and would like to give your opinions, please contact the writer. If you have any industrial and technical issues, please join the community for further discussion.
